Student of Artificial Intelligence, FPT University
Artificial Intelligence Student · Research Assistant
Hi, I am Nguyen Minh Nhut.
I design multimodal and human-centered AI systems that help machines understand emotion, speech, and intent. At FPT University (Ho Chi Minh campus) I focus on cross-modal learning, graph neural networks, and robust speech processing.
Research Focus
Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Building cross-modal fusion pipelines (audio, text, vision) with graph attention and adaptive attention to decode expressive cues.
Speech & Audio Intelligence
Exploring robust representation learning for emotion, speaker traits, and conversational analytics on top of transformer encoders.
Human-Centered AI
Designing interfaces, datasets, and evaluation loops that keep people at the center of intelligent systems and build trust.
Currently Exploring
-
Emotion in Conversational Contexts — modeling emotional dynamics throughout human-AI dialogue, enabling systems to perceive, track, and adapt to affective cues in real-time conversations.
-
Scalable Graph-Based Multimodal Architectures — designing efficient graph neural networks for real-time inference across heterogeneous modalities (speech, text, and vision) in emotionally rich interactions.
-
Semi-Supervised and Contrastive Learning Paradigms — leveraging unlabeled multimodal data to improve model robustness and generalization under limited annotation scenarios.
News
Selected Papers
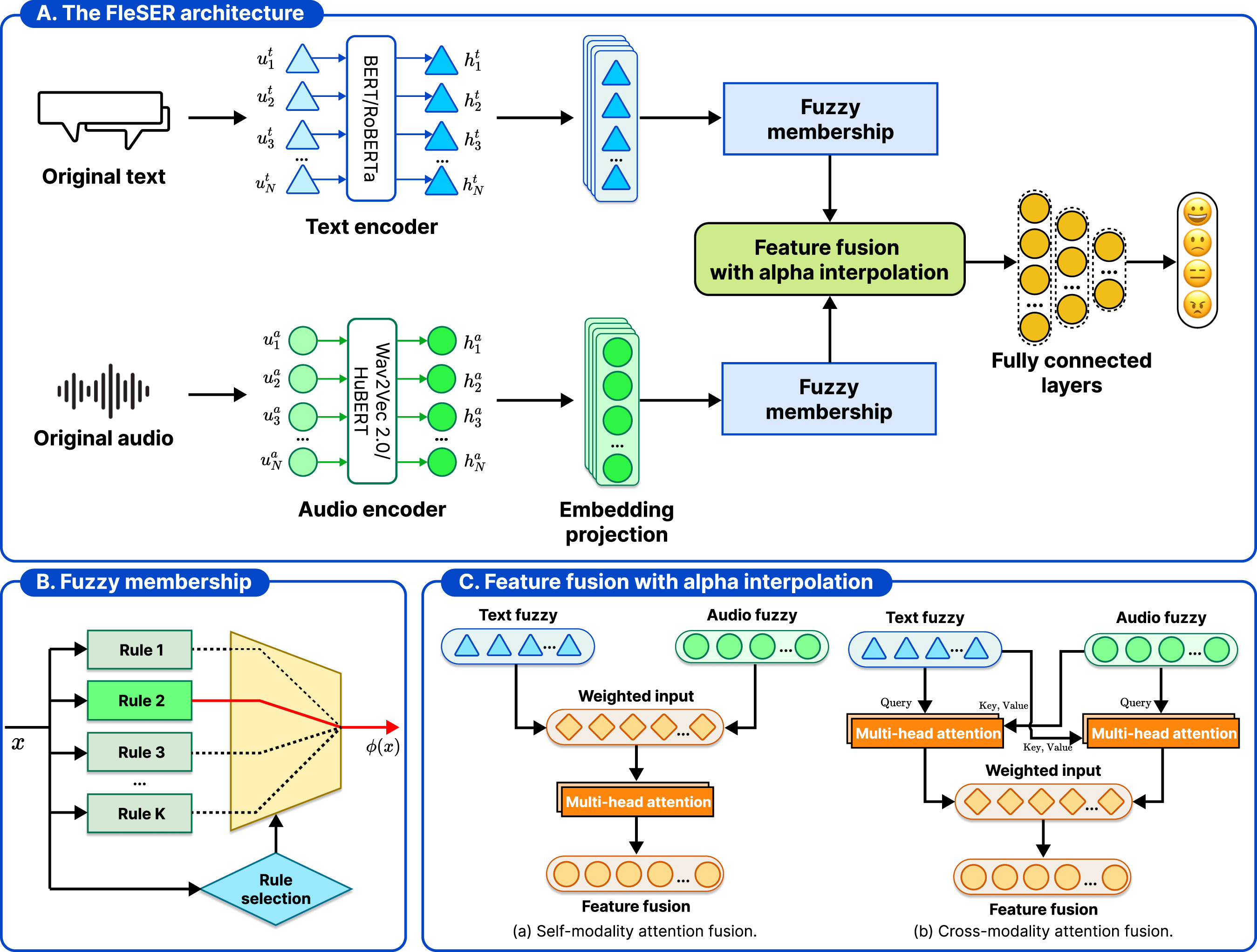
- Enhancing multimodal emotion recognition with dynamic fuzzy membership and attention fusionEngineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Feb 2026
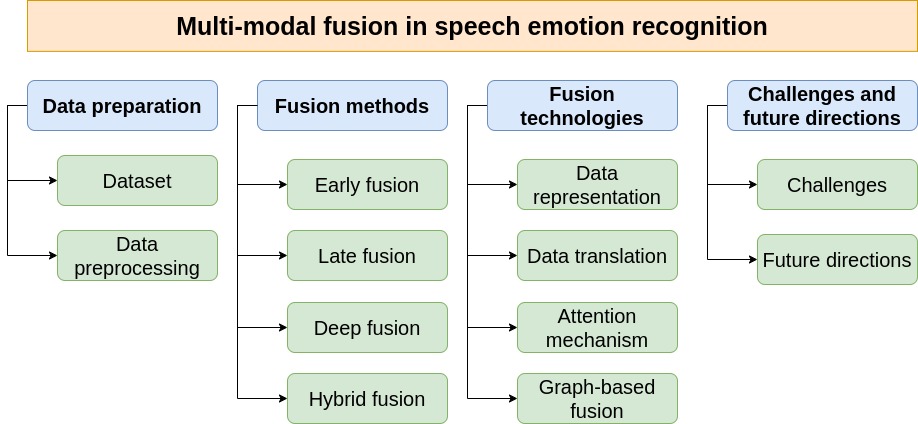
- Multimodal fusion in speech emotion recognition: A comprehensive review of methods and technologiesEngineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Jan 2026
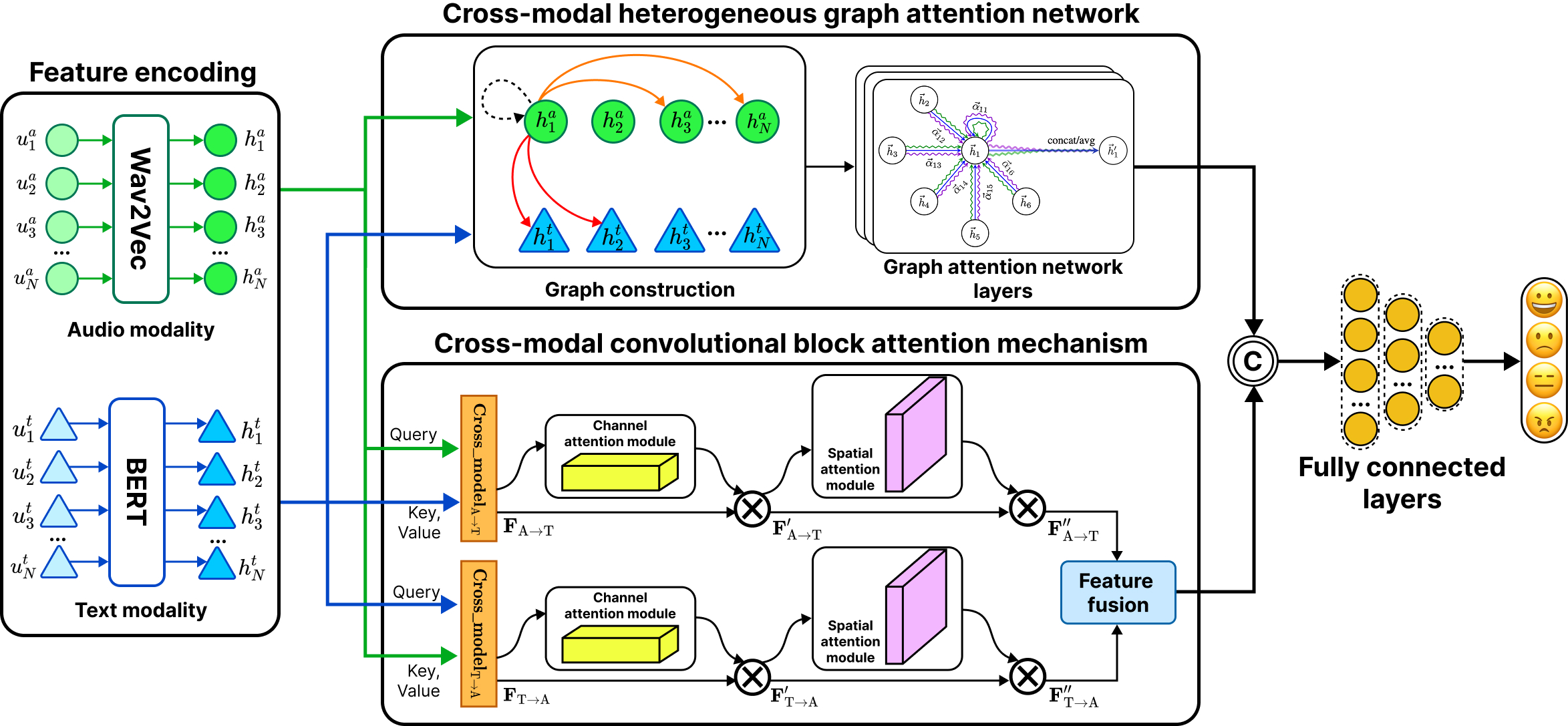
- In 2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Sep 2025