Publications
(†) denotes equal contribution
(*) denotes correspondance
denotes journal
denotes conference
denotes preprint
2026
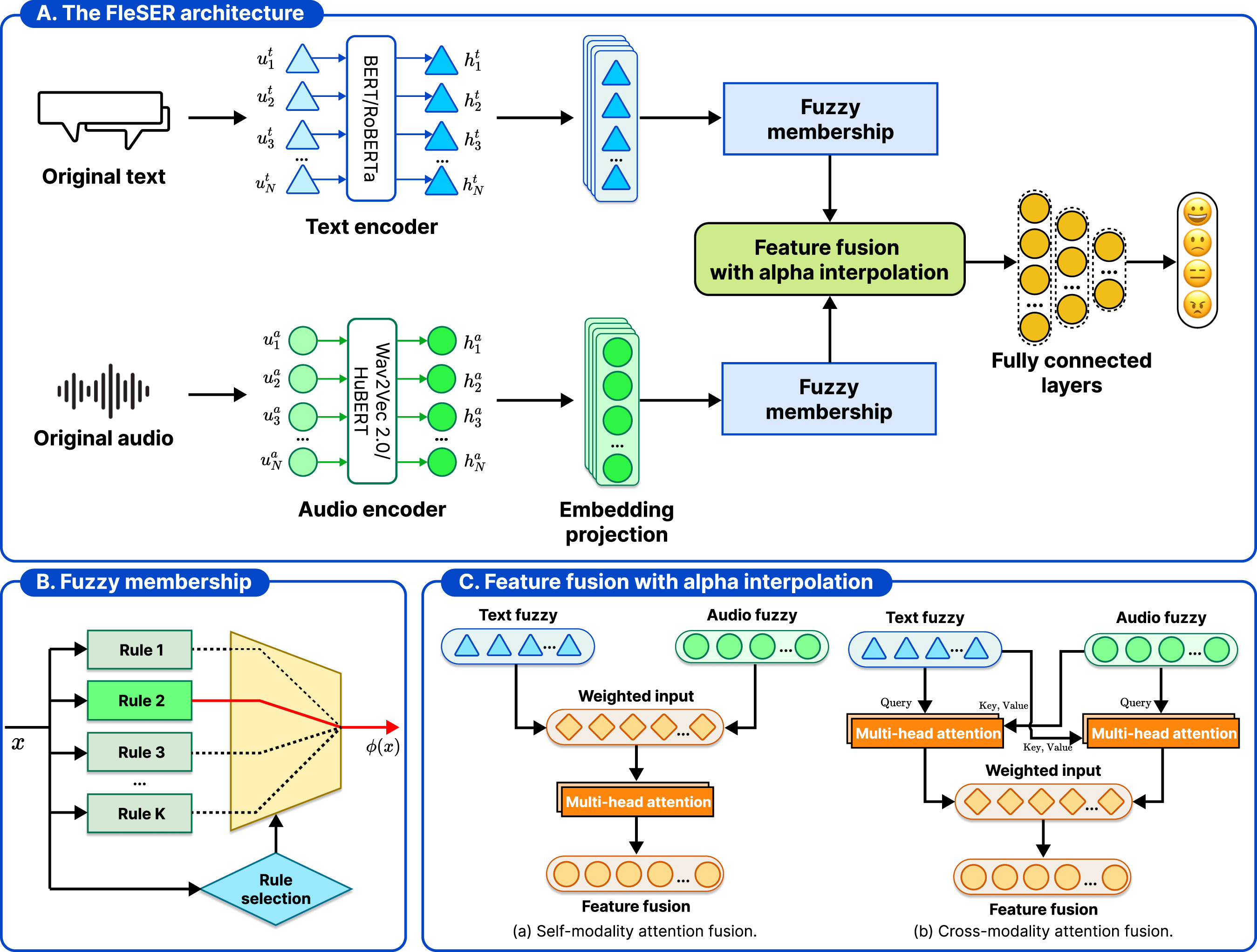
- Enhancing multimodal emotion recognition with dynamic fuzzy membership and attention fusionNhut Minh Nguyen, Minh Trung Nguyen, Thanh Trung Nguyen, and 6 more authorsEngineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Feb 2026
Multimodal learning has been shown to enhance classification outcomes in speech emotion recognition (SER). Despite this advantage, multimodal approaches in SER often face key challenges, including limited robustness to uncertainty, difficulty generalizing across diverse emotional contexts, and inefficiencies in integrating heterogeneous modalities. To overcome these constraints, we propose a multimodal emotion recognition architecture, named FleSER, which leverages dynamic fuzzy membership and attention-based fusion. Unlike most previous SER studies that apply fuzzy logic at the decision level, FleSER introduces a feature-level, rule-based dynamic fuzzy membership mechanism that adaptively refines modality representations prior to fusion. The FleSER architecture leverages audio and textual modalities, employing self-modality and cross-modality attention mechanisms with the α interpolation to capture complementary emotional cues. The α interpolation-based feature fusion mechanism adaptively emphasizes the more informative modality across varying contexts, ensuring robust multimodal integration. This comprehensive design enhances recognition accuracy. We evaluate FleSER on multiple benchmark datasets, surpassing previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches and demonstrating superior effectiveness in emotion recognition. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of each key component, including unimodal and multimodal input effectiveness, fuzzy membership functions, fusion strategies, and the projection dimension, on the performance of the FleSER architecture.
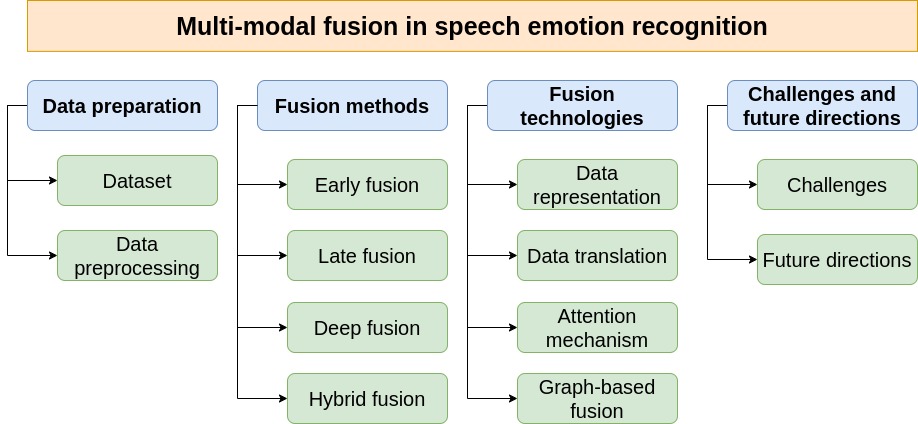
@article{nguyen2026fleser, title = {Enhancing multimodal emotion recognition with dynamic fuzzy membership and attention fusion}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Nguyen, Minh Trung and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Tran, Phuong-Nam and Pham, Nhat Truong and Le, Linh and Othmani, Alice and Saddik, Abdulmotaleb El and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, journal = {Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence}, year = {2026}, month = feb, doi = {10.1016/j.engappai.2025.113396}, preprint = {false}, google_scholar_id = {WF5omc3nYNoC}, dimensions = {true} } - Multimodal fusion in speech emotion recognition: A comprehensive review of methods and technologiesNhut Minh Nguyen, Thanh Trung Nguyen, Phuong-Nam Tran, and 3 more authorsEngineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Jan 2026
Speech emotion recognition (SER) plays a crucial role in human-computer interaction, enhancing numerous applications such as virtual assistants, healthcare monitoring, and customer support by identifying and interpreting emotions conveyed through spoken language. While single-modality SER systems demonstrate notable simplicity and computational efficiency, excelling in extracting critical features like vocal prosody and linguistic content, there is a pressing need to improve their performance in challenging conditions, such as noisy environments and the handling of ambiguous expressions or incomplete information. These challenges underscore the necessity of transitioning to multi-modal approaches, which integrate complementary data sources to achieve more robust and accurate emotion detection. With advancements in artificial intelligence, especially in neural networks and deep learning, many studies have employed advanced deep learning and feature fusion techniques to enhance SER performance. This review synthesizes comprehensive publications from 2020 to 2024, exploring prominent multi-modal fusion strategies, including early fusion, late fusion, deep fusion, and hybrid fusion methods, while also examining data representation, data translation, attention mechanisms, and graph-based fusion technologies. We assess the effectiveness of various fusion techniques across standard SER datasets, highlighting their performance in diverse tasks and addressing challenges related to data alignment, noise management, and computational demands. Additionally, we explore potential future directions for enhancing multi-modal SER systems, emphasizing scalability and adaptability in real-world applications. This survey aims to contribute to the advancement of multi-modal SER and to inform researchers about effective fusion strategies for developing more responsive and emotion-aware systems.
@article{nguyen2025MSER, bibtex_show = true, title = {Multimodal fusion in speech emotion recognition: A comprehensive review of methods and technologies}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Tran, Phuong-Nam and Lim, Chee Peng and Pham, Nhat Truong and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, journal = {Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence}, year = {2026}, month = jan, doi = {10.1016/j.engappai.2025.112624}, google_scholar_id = {_FxGoFyzp5QC}, dimensions = {true} }
2025
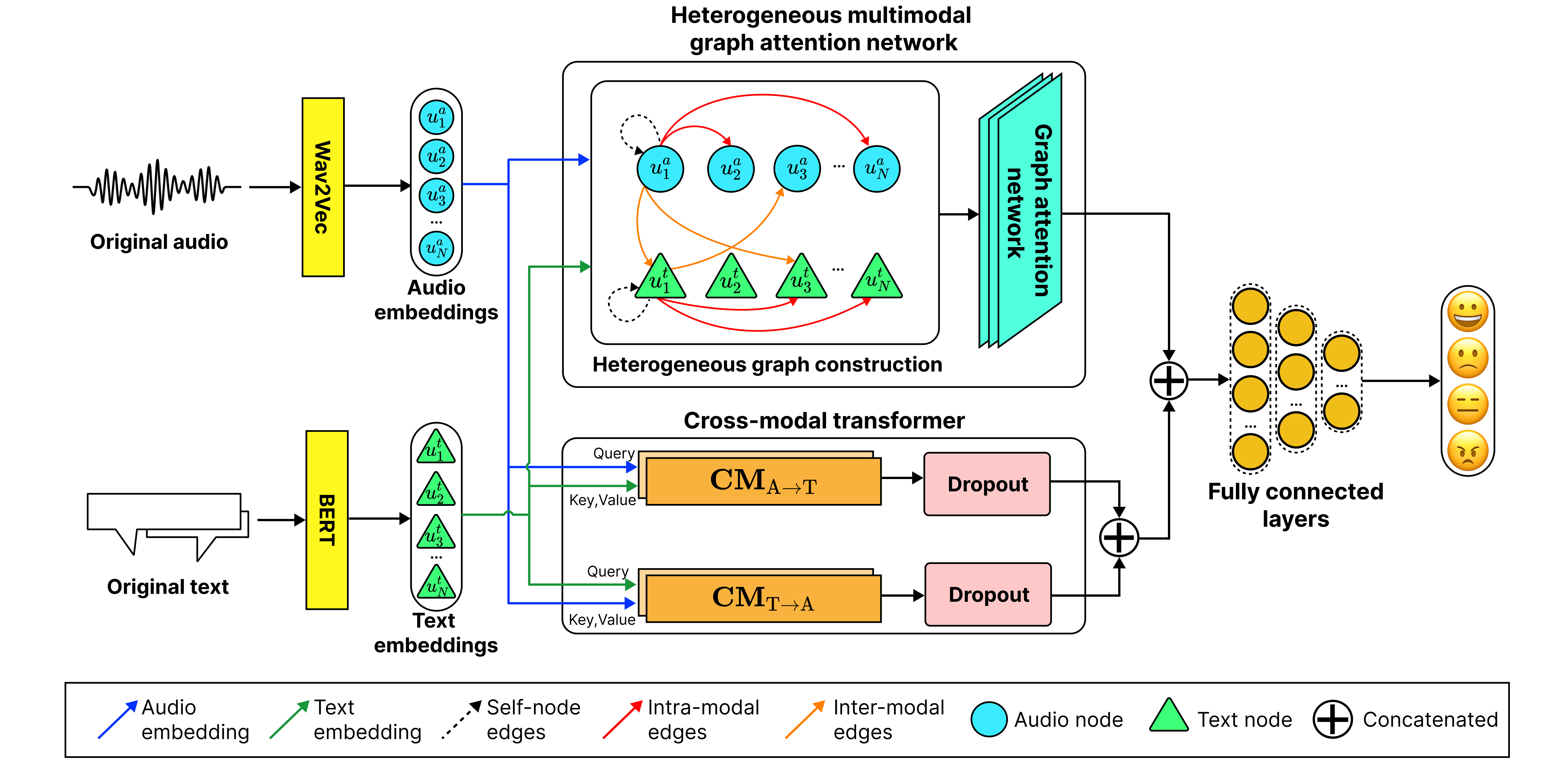
- HemoGAT: Heterogeneous Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition with Cross-Modal Transformer and Graph Attention NetworkNhut Minh Nguyen, Thanh Trung Nguyen, and Duc Ngoc Minh DangAdvances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Jan 2025To appear
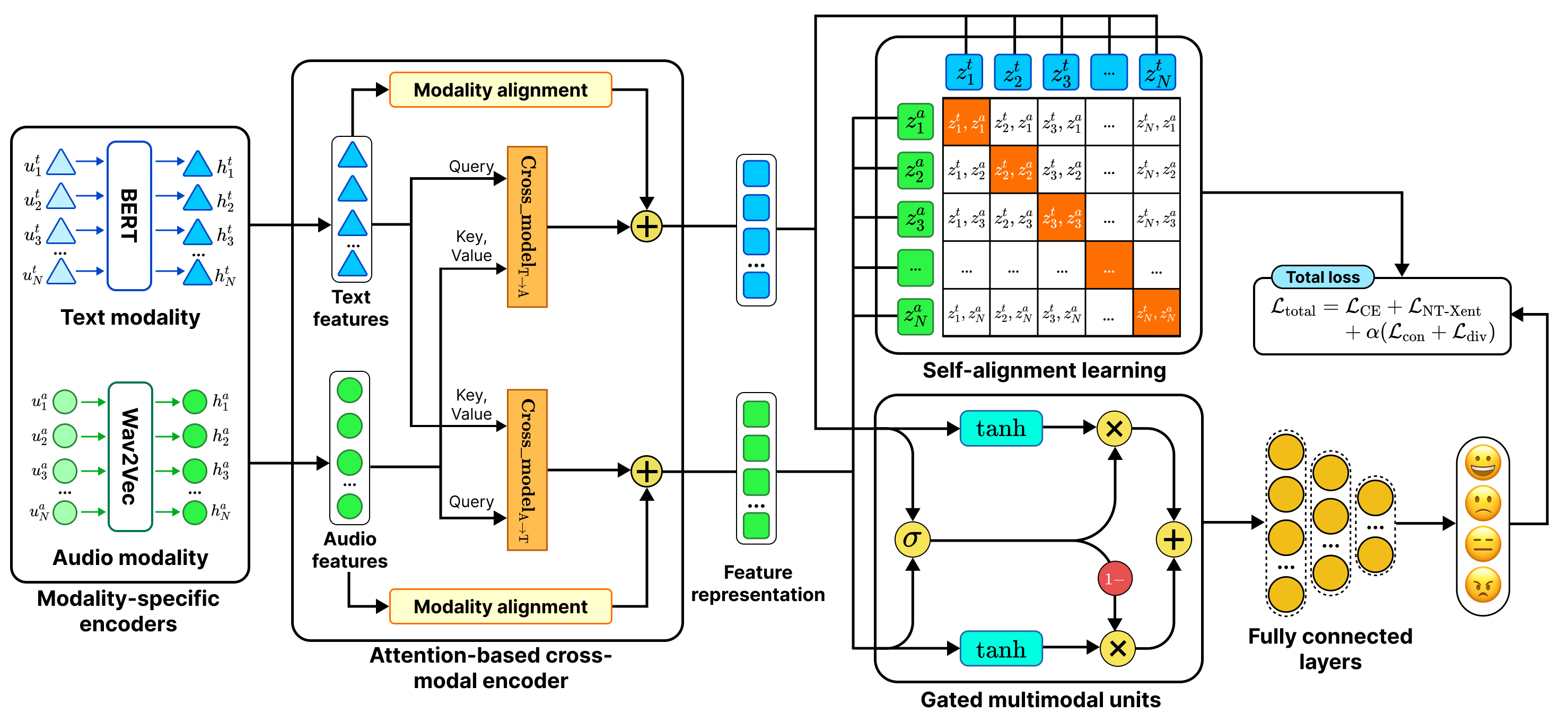
@article{nguyen2026HemoGAT, bibtex_show = true, title = {HemoGAT: Heterogeneous Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition with Cross-Modal Transformer and Graph Attention Network}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, journal = {Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering}, year = {2025}, note = {To appear}, } - GloMER: Towards Robust Multimodal Emotion Recognition via Gated Fusion and Contrastive LearningNhut Minh Nguyen, Duc Tai Phan, and Duc Ngoc Minh DangIn The 17th International Conference on Management of Digital Ecosystem (MEDES 2025), Nov 2025To appear
@inproceedings{nguyen2025GloMER, bibtex_show = true, title = {GloMER: Towards Robust Multimodal Emotion Recognition via Gated Fusion and Contrastive Learning}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Phan, Duc Tai and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, booktitle = {The 17th International Conference on Management of Digital Ecosystem (MEDES 2025)}, year = {2025}, month = nov, address = {Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam}, organization = {FPT University}, dimensions = {false}, note = {To appear} } - DAAL: Dual Ambiguity in Active Learning for Object Detection with YOLOEDuc Tai Phan, Nhut Minh Nguyen, and Duc Ngoc Minh DangIn The 17th International Conference on Management of Digital Ecosystem (MEDES 2025), Nov 2025To appear
@inproceedings{Phan2025DAAL, bibtex_show = true, title = {DAAL: Dual Ambiguity in Active Learning for Object Detection with YOLOE}, author = {Phan, Duc Tai and Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, booktitle = {The 17th International Conference on Management of Digital Ecosystem (MEDES 2025)}, year = {2025}, month = nov, address = {Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam}, organization = {FPT University}, dimensions = {false}, note = {To appear} } - Nhut Minh Nguyen, Thu Thuy Le, Thanh Trung Nguyen, and 3 more authorsIn 2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Sep 2025
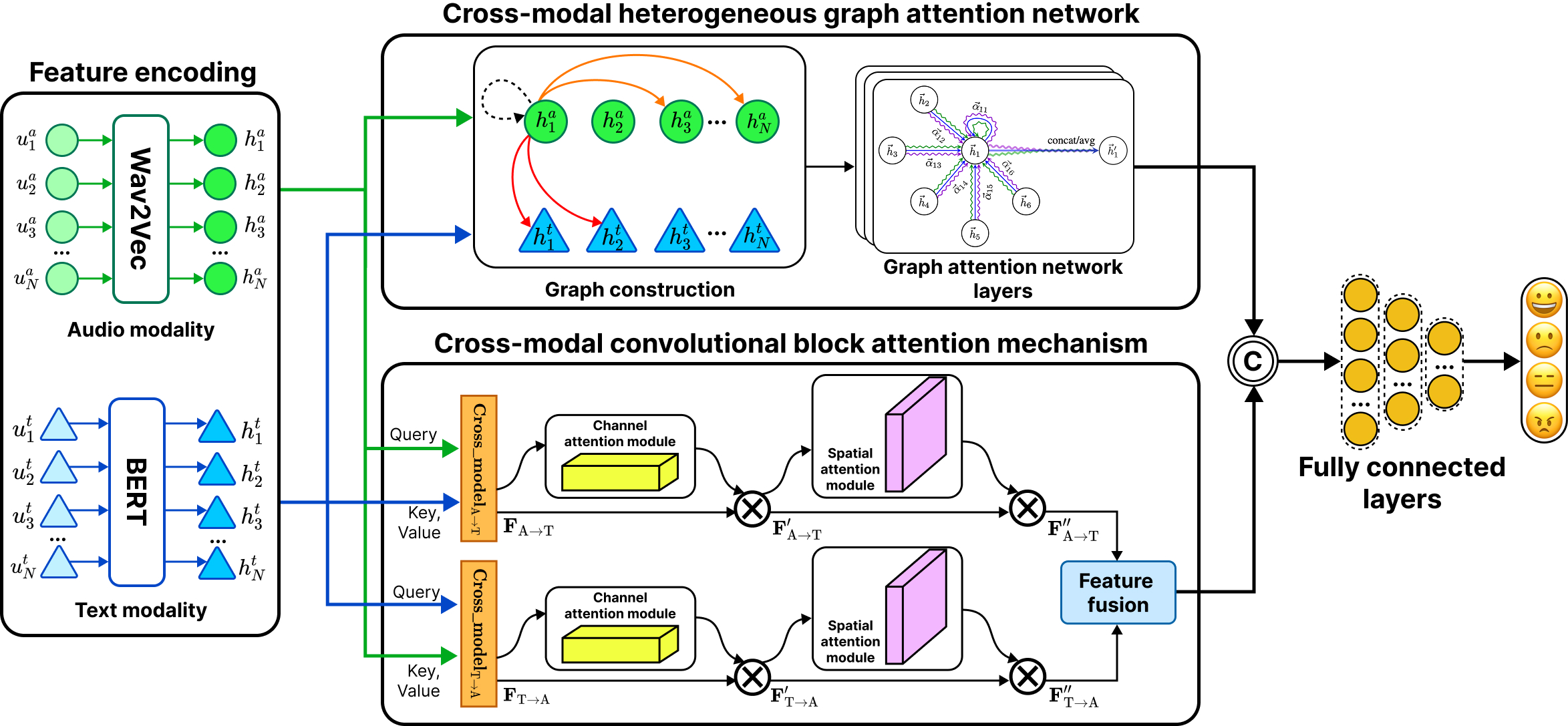
Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) offers significant advantages over unimodal approaches by integrating diverse information streams such as audio and text. However, effectively fusing these heterogeneous modalities remains a significant challenge. We propose CemoBAM, a novel dualstream architecture that effectively integrates the Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network (CH-GAT) with the Cross-modal Convolutional Block Attention Mechanism (xCBAM). In CemoBAM architecture, the CH-GAT constructs a heterogeneous graph that models intra- and inter-modal relationships, employing multi-head attention to capture fine-grained dependencies across audio and text feature embeddings. The xCBAM enhances feature refinement through a cross-modal transformer with a modified 1D-CBAM, employing bidirectional cross-attention and channel-spatial attention to emphasize emotionally salient features. The CemoBAM architecture surpasses previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods by 0.32% on IEMOCAP and 3.25% on ESD datasets. Comprehensive ablation studies validate the impact of Top-K graph construction parameters, fusion strategies, and the complementary contributions of both modules. The results highlight CemoBAM’s robustness and potential for advancing multimodal SER applications.
@inproceedings{nguyen2025CemoBAM, bibtex_show = true, title = {CemoBAM: Advancing Multimodal Emotion Recognition through Heterogeneous Graph Networks and Cross-Modal Attention Mechanisms}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Le, Thu Thuy and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Phan, Duc Tai and Tran, Anh Khoa and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, booktitle = {2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS)}, doi = {10.23919/apnoms67058.2025.11181320}, year = {2025}, month = sep, address = {Kaohsiung, Taiwan}, organization = {National Sun Yat-sen University}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {qjMakFHDy7sC} } - ALMUS: Enhancing Active Learning for Object Detection with Metric-Based Uncertainty SamplingDuc Tai Phan, Nhut Minh Nguyen, Khang Phuc Nguyen, and 2 more authorsIn 2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Sep 2025
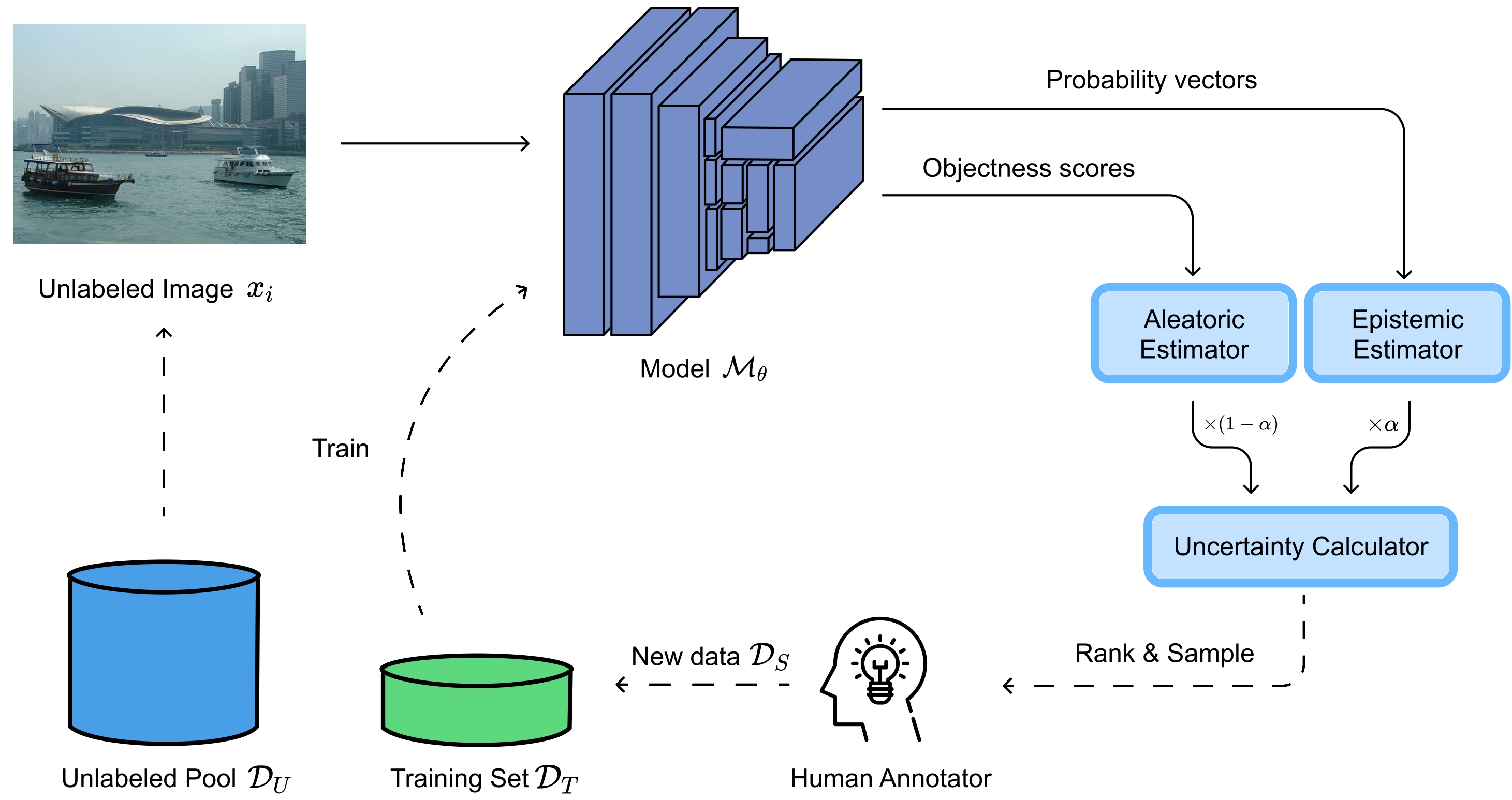
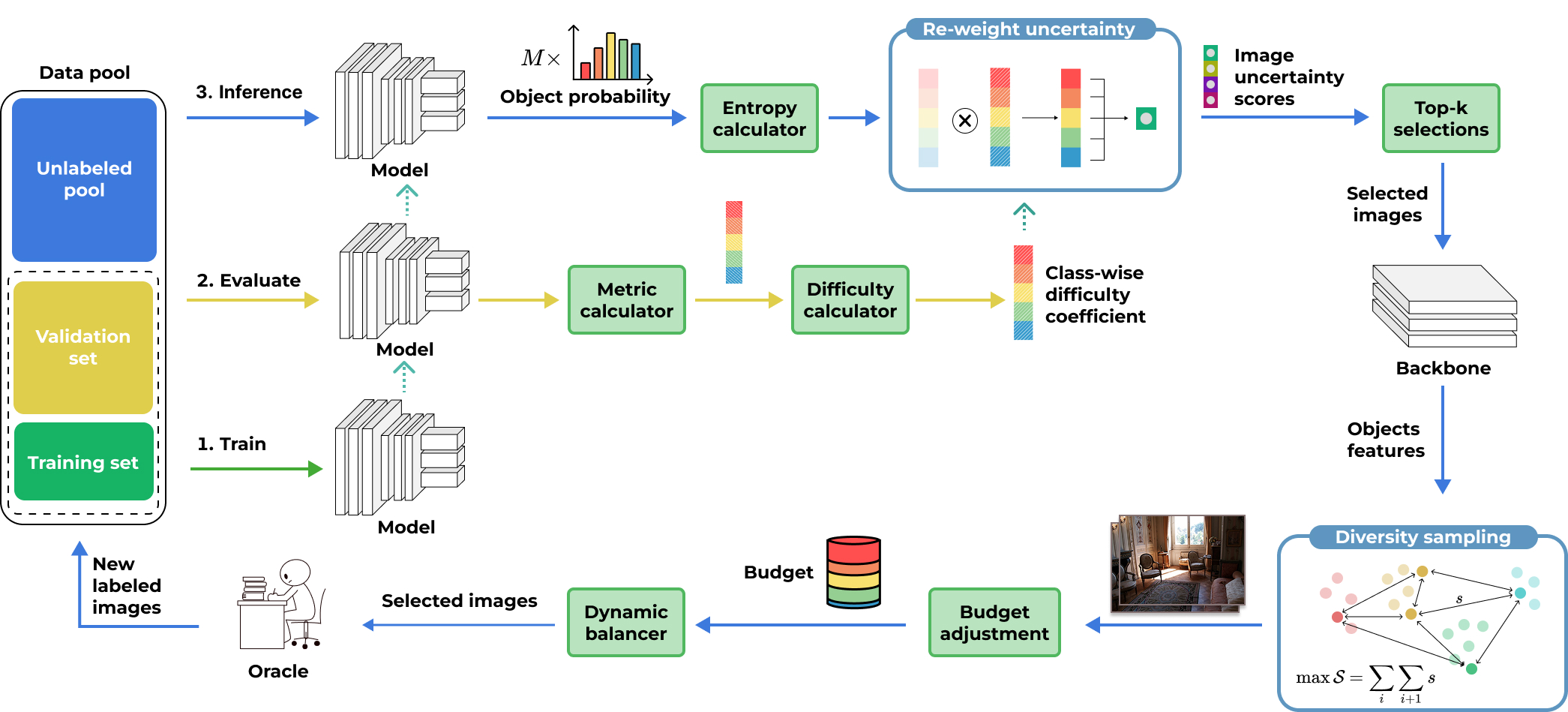
Object detection is critical in computer vision but often requires large amounts of labeled data for effective training. Active learning (AL) has emerged as a promising solution to reduce the annotation burden by selecting the most informative samples for labeling. However, existing AL methods for object detection primarily focus on uncertainty sampling, which may not effectively balance the dual challenges of classification and localization. In this study, we explore active learning for object detection, with the objective of optimizing model performance while substantially reducing the demand for annotated data. We propose a novel Active Learning with Metric-based Uncertainty Sampling (ALMUS) that works effectively for the object detection task. This approach prioritizes selecting images containing objects from categories where the model exhibits suboptimal performance, as determined by category-specific evaluation metrics. To balance the annotation budget across different object classes, we propose a dynamic allocation strategy that considers the difficulty of each class and the distribution of object instances within the dataset. This combination of strategies enables our method to effectively address the dual challenges of classification and localization in object detection tasks while still focusing on the rarest and most challenging classes. We conduct extensive experiments on the PASCAL VOC 2007 and 2012 datasets, demonstrating that our method outperforms several active learning baselines. Our results indicate that the proposed approach enhances model performance and accelerates convergence, making it a valuable contribution to the field of active learning in object detection.
@inproceedings{phan2025ALMUS, bibtex_show = true, title = {ALMUS: Enhancing Active Learning for Object Detection with Metric-Based Uncertainty Sampling}, author = {Phan, Duc Tai and Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Nguyen, Khang Phuc and Pham, Tri and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, booktitle = {2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS)}, doi = {10.23919/apnoms67058.2025.11181447}, year = {2025}, month = sep, address = {Kaohsiung, Taiwan}, organization = {National Sun Yat-sen University}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {UeHWp8X0CEIC} } - YOLO-Powered Traffic Sign Detection and OpenStreetMap Integration for Intelligent NavigationDuc-Hieu Hoang, Dinh Thuan Nguyen, Quoc Huy Tran, and 3 more authorsIn 2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Sep 2025
This study presents the development of a deep learning-based traffic sign recognition system integrated with OpenStreetMap (OSM) to enhance smart navigation and traffic management. The system utilizes a You Only Look Once (YOLO)based model trained on the Vietnamese Camera-based Traffic Sign Recognition 47 (VCTSR47) dataset to detect and classify Vietnamese traffic signs accurately. A dashboard camera mounted on motorbikes or cars collects real-world traffic data, automatically recognizing traffic signs, extracting Global Positioning System (GPS) coordinates, and storing relevant information in a structured database. The extracted data is integrated into OSM via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), enabling precise visualization and real-time alerts for critical traffic signs. The system’s performance is rigorously evaluated through various metrics, including mean Average Precision (mAP), Precision, Recall, and Frames Per Second (FPS). Experimental results confirm high recognition accuracy and real-time processing efficiency, demonstrating the feasibility and potential applications of deep learning and digital mapping in modern intelligent transportation systems.
@inproceedings{hoang2025yolo, bibtex_show = true, title = {YOLO-Powered Traffic Sign Detection and OpenStreetMap Integration for Intelligent Navigation}, author = {Hoang, Duc-Hieu and Nguyen, Dinh Thuan and Tran, Quoc Huy and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, doi = {10.23919/apnoms67058.2025.11181312}, booktitle = {2025 Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS)}, year = {2025}, month = sep, address = {Kaohsiung, Taiwan}, organization = {National Sun Yat-sen University}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {IjCSPb-OGe4C} }
2024
- Voice-Based Age and Gender Recognition: A Comparative Study of LSTM, RezoNet and Hybrid CNNs-BiLSTM ArchitectureNhut Minh Nguyen, Thanh Trung Nguyen, Hua Hiep Nguyen, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 15th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Sep 2024
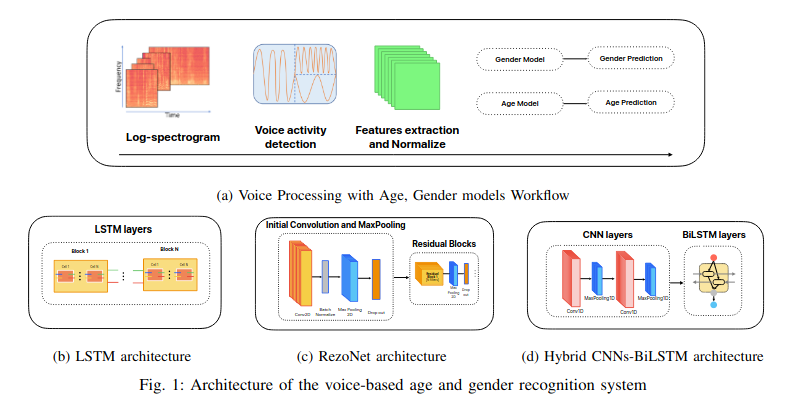
In this study, we compared three architectures for the task of age and gender recognition from voice data: Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTM), Hybrid of Convolutional Neural Networks and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (CNNs-BiLSTM), and the recently released RezoNet architecture. The dataset used in this study was sourced from Mozilla Common Voice in Japanese. Features such as pitch, magnitude, Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), and filter-bank energies were extracted from the voice data for signal processing, and the three architectures were evaluated. Our evaluation revealed that LSTM was slightly less accurate than RezoNet (83.1%), with the hybrid CNNs-BiLSTM (93.1%) and LSTM achieving the highest accuracy for gender recognition (93.5%). However, hybrid CNNs-BiLSTM architecture outperformed the other models in age recognition, achieving an accuracy of 69.75%, compared to 64.25% and 44.88% for LSTM and RezoNet, respectively. Using Japanese language data and the extracted characteristics, the hybrid CNNs-BiLSTM architecture model demonstrated the highest accuracy in both tests, highlighting its efficacy in voice-based age and gender detection. These results suggest promising avenues for future research and practical applications in this field.
@inproceedings{nguyen2024age-gender, bibtex_show = true, title = {Voice-Based Age and Gender Recognition: A Comparative Study of LSTM, RezoNet and Hybrid CNNs-BiLSTM Architecture}, author = {Nguyen, Nhut Minh and Nguyen, Thanh Trung and Nguyen, Hua Hiep and Tran, Phuong-Nam and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, booktitle = {2024 15th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC)}, pages = {1--1}, year = {2024}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ICTC62082.2024.10827387}, dimensions = {true}, google_scholar_id = {d1gkVwhDpl0C}, }